 The sum of the interior angles of a simple n-gon is (n − 2)π radians or 180n − 360 degrees. This is because any simple n-gon can be considered to be made up of (n − 2) triangles, each of which has an angle sum of π radians or 180 degrees. The measure of any interior angle of a convex regular n-gon is
The sum of the interior angles of a simple n-gon is (n − 2)π radians or 180n − 360 degrees. This is because any simple n-gon can be considered to be made up of (n − 2) triangles, each of which has an angle sum of π radians or 180 degrees. The measure of any interior angle of a convex regular n-gon is  radians or
radians or  degrees.
degrees.The interior angles of regular star polygons were first studied by Poinsot, in the same paper in which he describes the four regular star polyhedra.
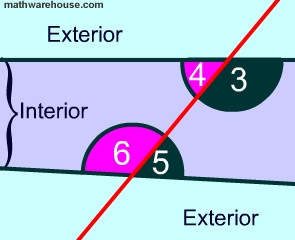
The exterior angle is the supplementary angle to the interior angle.
~Hidayah


